Eyes are one of the most essential organs in our body, so it’s important to take good care of them through proper habits like regular exercises and eating eye-friendly foods. Sometimes, issues like cysts can develop, which are small, enclosed structures made up of tissue filled with liquid, semi-solid material, blood, or gas. These cysts aren’t part of normal tissue and can occur in anyone, regardless of age.
When a cyst develops on either the upper or lower eyelid, it’s referred to as an eye cyst or chalazion. These cysts can also be known as conjunctival granulomas, tarsal cysts, or meibomian cysts. One of the most common causes of an eye cyst is a bacterial infection that blocks the oil glands in the eyelid. These cysts can vary in size and may cause discomfort, infection, or even remain harmless without symptoms.
In some cases, larger cysts can lead to vision problems. If you experience an eye cyst, it’s crucial to avoid rubbing the affected area as this can worsen redness and irritation. Consulting a doctor for proper treatment is key, as the condition may differ from person to person.
### Causes of Eye Cysts
Eye cysts are triggered by different factors, including blockages in the meibomian glands, skin conditions like keratosis, skin tags, styes, poor hygiene, old or expired makeup products, bacteria, or even skin cancer. The meibomian glands along the eyelashes produce oil that works together with tears to lubricate the eyes. When one of these glands gets clogged, it can lead to the formation of an eye cyst. Recurring cysts can also be linked to acne or other skin issues. In some cases, doctors may recommend a biopsy to rule out cancer if such cysts persist.
### Symptoms of Eye Cysts
Eye cysts can appear suddenly, either with or without warning signs. They can cause pain, irritation, or simply create a noticeable bump. It’s advised not to touch or rub the area since this can worsen the irritation. Eye cysts are generally not contagious or cancerous, but common symptoms include:
– Mild pain and irritation
– Swelling of the eyelid
– Redness and tenderness of the eyelid
– Discomfort when blinking
– Discharge from the eye
– Gradually enlarging lumps
– Sensitivity to light
– Pressure in the eye
– Loss of eyelashes near the affected area
In more severe cases, other symptoms like extreme eye swelling, intense pain, blurry or double vision, severe headaches, high fever, and excessive discharge require immediate medical attention.
### Types of Eye Cysts
1. **Skin Tags**: These are harmless skin growths that can sometimes form where the eyelid meets the eye shaft. If necessary, they can be removed surgically.
2. **Styes**: Often caused by blocked oil glands, styes are red, tender bumps that usually resolve within 24–72 hours with proper care. If untreated or persistent, they may not fall into this category.
3. **Meibomian Cysts**: These develop due to leftover debris in the eye following an infection, resulting in blocked oil glands. Patients with this type of cyst experience swelling and discomfort.
4. **Inclusion Cysts**: These are painless white swellings on the eyelid. Although harmless, it’s still advisable to consult a doctor.
5. **Sweat Gland Cysts**: Found near the tear ducts, these rounded, shiny, and transparent cysts are among the most common types.
6. **Nevus**: These are flesh-colored growths that appear on the eyelids.
### Treatment and Removal
Some meibomian cysts resolve on their own. However, if a cyst doesn’t improve, becomes very large, disrupts vision, or causes significant pain, a doctor may suggest surgical removal. This procedure, performed by an ophthalmologist, involves draining the cyst using a small incision under local anesthesia. The area heals quickly, with no stitches required, and an antibiotic ointment is applied afterward to prevent infection.
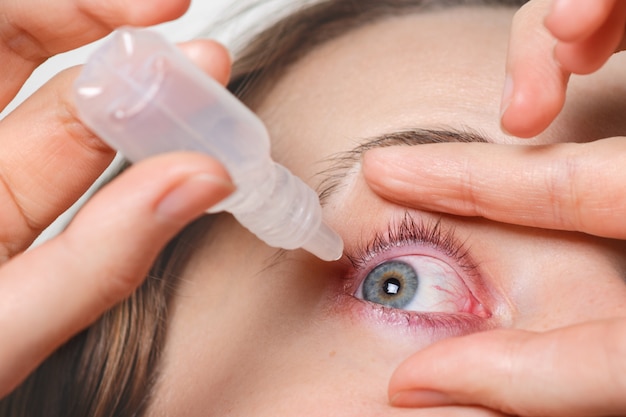
Other remedies include good hygiene practices, using prescribed antibiotic eye drops, applying warm compresses to the area, washing hands thoroughly before handling the eyes, and always using clean towels. For recurring cysts, steroid injections may be recommended, and biopsies might be needed to rule out cancer. Regularly washing the eyes with mild soap can also help prevent the blockage of oil glands.
### Prevention Tips
– Avoid wearing contact lenses until eye swelling goes down.
– Refrain from using eyeliners and mascaras until symptoms disappear.
– Always remove makeup before bed.
– Maintain proper eye hygiene by cleaning them regularly.
– Avoid scratching or draining the cyst yourself, as this can worsen the condition.
– Follow a healthy diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, flaxseed oil, and vegetables to support overall eye health.